Technical Interview Questions In Networking For Freshers and Experienced
We have compiled the most frequently asked Interview questions in networking that will help you to prepare for the Interview questions in networking that an interviewer might ask you during your interview.
A network is a set of devices that are connected with a physical media link. In a network, two or more nodes are connected by a physical link, or two or more networks are connected by one or more nodes. A network is a collection of devices connected to each other to allow the sharing of data.
An example of a network is the internet. The internet connects millions of people across the world.
Two or more computers are connected directly by an optical fiber or any other cable. A node is a point where a connection is established. It is a network component that is used to send, receive, and forward electronic information.
A device connected to a network has also termed a Node. Let’s consider that in a network there are 2 computers, 2 printers, and a server are connected, then we can say that there are five nodes on the network. 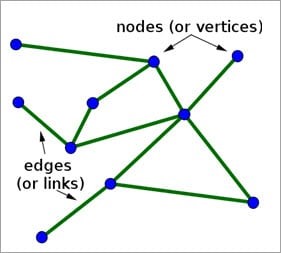
• Hub: Hub will broadcast all data to every port. It has a common connection point for all devices.
• Switch: Switch will create a dynamic connection and provide information to the requesting port.
• Router: The router is the device that will be responsible for forwarding data packets.
A list of advantages of distributed processing:
Secure
• Support Encapsulation
• Distributed database
• Faster Problem solving
• Security through redundancy
• Collaborative Processing
Open System Interconnection, the name itself suggests that it is a reference model that defines how applications can communicate with each other over a networking system.
It also helps to understand the relationship between networks and defines the process of communication in a network.
• Network reliability: Network reliability means the ability of the network to carry out the desired operation through a network such as communication through a network.
• Network reliability plays a significant role in network functionality. The network monitoring systems and devices are the essential requirements for making the network reliable. The network monitoring system identifies the problems that are occurred in the network while the network devices ensure that data should reach the appropriate destination.
• The reliability of a network can be measured by the following factors:
• Downtime: The downtime is defined as the required time to recover.
• Failure Frequency: It is the frequency when it fails to work the way it is intended.
• Catastrophe: It indicates that the network has been attacked by some unexpected event such as fire, earthquake.
Given below are the seven layers of OSI Reference Models:
• Physical Layer (Layer 1): It converts data bits into electrical impulses or radio signals.
• Data Link Layer (Layer 2): At the Data Link layer, data packets are encoded and decoded into bits and it provides a node to node data transfer. This layer also detects the errors that occurred at Layer 1.
• Network Layer (Layer 3): This layer transfers variable length data sequence from one node to another node in the same network. This variable-length data sequence is also known as “Datagrams”.
• Transport Layer (Layer 4): It transfers data between nodes and also provides acknowledgment of successful data transmission. It keeps track of transmission and sends the segments again if the transmission fails.
• Session Layer (Layer 5): This layer manages and controls the connections between computers. It establishes, coordinates, exchanges, and terminates the connections between local and remote applications.
• Presentation Layer (Layer 6): It is also called a “Syntax Layer”. Layer 6 transforms the data into the form in which the application layer accepts.
• Application Layer (Layer 7): This is the last layer of the OSI Reference Model and is the one that is close to the end-user. Both end-user and application layer interacts with the software application. This layer provides services for email, file transfer, etc.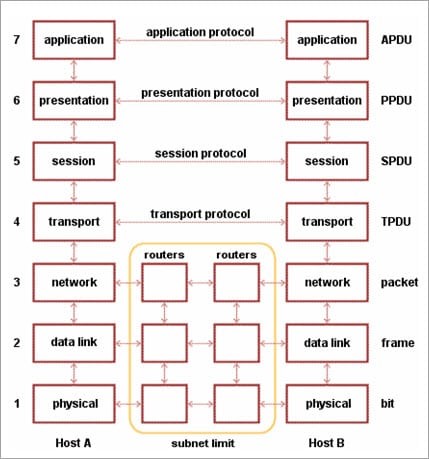
There is mainly two security affecting factors:
Unauthorized Access
Viruses
The most widely used and available protocol is TCP/IP i.e. Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol. TCP/IP specifies how data should be packaged, transmitted, and routed in their end to end data communication.
There are four layers as shown in the below diagram: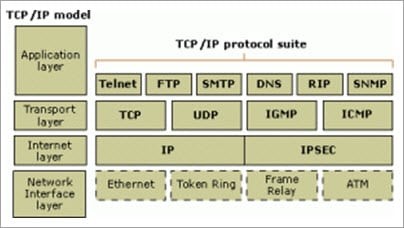
Given below is a brief explanation of each layer:
• Application Layer: This is the top layer in the TCP/IP model. It includes processes that use the Transport Layer Protocol to transmit the data to their destination. There are different Application Layer Protocols such as HTTP, FTP, SMTP, SNMP protocols, etc.
• Transport Layer: It receives the data from the Application Layer which is above the Transport Layer. It acts as a backbone between the host’s system connected with each other and it mainly concerns about the transmission of data. TCP and UDP are mainly used as Transport Layer protocols.
• Network or Internet Layer: This layer sends the packets across the network. Packets mainly contain source & destination IP addresses and actual data to be transmitted.
• Network Interface Layer: It is the lowest layer of the TCP/IP model. It transfers the packets between different hosts. It includes encapsulation of IP packets into frames, mapping IP addresses to physical hardware devices, etc.
The following factors affect the performance of a network:
• Large number of users
• Transmission medium types
• Hardware
• Software
A link refers to the connectivity between two devices. It includes the type of cables and protocols used for one device to be able to communicate with the other.
There are 4 major types of networks.
Let’s take a look at each of them in detail.
Personal Area Network (PAN): It is the smallest and basic network type that is often used at home. It is a connection between the computer and another device such as a phone, printer, modem tablets, etc
Local Area Network (LAN): LAN is used in small offices and Internet cafes to connect a small group of computers to each other. Usually, they are used to transfer a file or for playing the game in a network.
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN): It is a powerful network type than LAN. The area covered by MAN is a small town, city, etc. A huge server is used to cover such a large span of area for connection.
Wide Area Network (WAN): It is more complex than LAN and covers a large span of the area typically a large physical distance. The Internet is the largest WAN which is spread across the world. WAN is not owned by any single organization but it has distributed ownership.
There are some other types of the network as well:
• Storage Area Network (SAN)
• System Area Network (SAN)
• Enterprise Private Network (EPN)
• Passive Optical Local Area Network (POLAN)
There are 7 OSI layers:
1) Physical Layer,
2) Data Link Layer,
3) Network Layer,
4) Transport Layer,
5) Session Layer,
6) Presentation Layer, and
7) Application Layer.
Routers can connect two or more network segments. These are intelligent network devices that store information in its routing tables, such as paths, hops, and bottlenecks. With this info, they can determine the best path for data transfer. Routers operate at the OSI Network Layer.
A subnet mask is combined with an IP address to identify two parts: the extended network address and the host address. Like an IP address, a subnet mask is made up of 32 bits.
A single segment of UTP cable has an allowable length of 90 to 100 meters. This limitation can be overcome by using repeaters and switches.
Data encapsulation is the process of breaking down information into smaller, manageable chunks before it is transmitted across the network. In this process that the source and destination addresses are attached to the headers, along with parity checks.
VPN is the Virtual Private Network and is built on the Internet as a private wide area network. Internet-based VPNs are less expensive and can be connected from anywhere in the world.
VPNs are used to connect offices remotely and are less expensive when compared to WAN connections. VPNs are used for secure transactions and confidential data can be transferred between multiple offices. VPN keeps company information secure against any potential intrusion.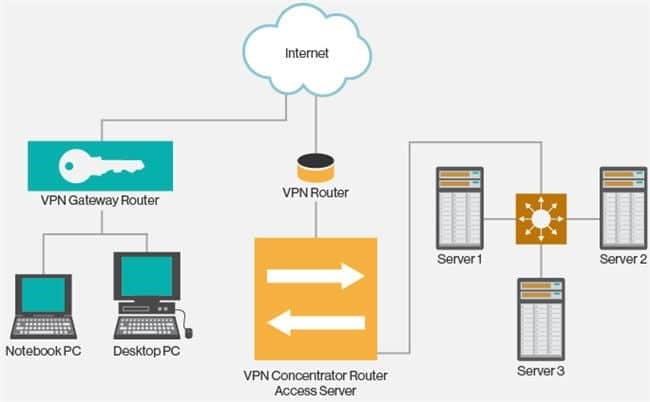
Given below are the 3 types of VPN’s:
Access VPN: Access VPN’s provide connectivity to mobile users and telecommuters. It is an alternative option for dial-up connections or ISDN connections. It provides low-cost solutions and a wide range of connectivity.
Intranet VPN: They are useful for connecting remote offices using shared infrastructure with the same policy as a private network.
Extranet VPN: Using shared infrastructure over an intranet, suppliers, customers, and partners are connected using dedicated connections.
Ipconfig stands for Internet Protocol Configuration and this command is used on Microsoft Windows to view and configure the network interface.
The command Ipconfig is useful for displaying all TCP/IP network summary information currently available on a network. It also helps to modify the DHCP protocol and DNS setting.
Ifconfig (Interface Configuration) is a command that is used on Linux, Mac, and UNIX operating systems. It is used to configure, control the TCP/IP network interface parameters from CLI i.e. Command Line Interface. It allows you to see the IP addresses of these network interfaces.
It refers to a direct connection between two computers on a network. A point to point connection does not need any other network devices other than connecting a cable to the NIC cards of both computers.
Name the different types of network topologies and brief their advantages?
Network Topology is nothing but the physical or logical way in which the devices (like nodes, links, and computers) of a network are arranged. Physical Topology means the actual place where the elements of a network are located.
Logical Topology deals with the flow of data over the networks. A link is used to connect more than two devices of a network. And more than two links located nearby form a topology.
Network topologies are classified as below:
a) Bus Topology: In Bus Topology, all the devices of the network are connected to a common cable (also called the backbone). As the devices are connected to a single cable, it is also termed as Linear Bus Topology.
The advantage of bus topology is that it can be installed easily. And the disadvantage is that if the backbone cable breaks then the whole network will be down.
b) Star Topology: In Star Topology, there is a central controller or hub to which every node or device is connected through a cable. In this topology, the devices are not linked to each other. If a device needs to communicate with the other, then it has to send the signal or data to the central hub. And then the hub sends the same data to the destination device.
The advantage of the star topology is that if a link breaks then only that particular link is affected. The whole network remains undisturbed. The main disadvantage of the star topology is that all the devices of the network are dependent on a single point (hub). If the central hub gets failed, then the whole network gets down.
c) Ring Topology: In Ring Topology, each device of the network is connected to two other devices on either side which in turn forms a loop. Data or Signal in ring topology flow only in a single direction from one device to another and reaches the destination node.
The advantage of ring topology is that it can be installed easily. Adding or deleting devices to the network is also easy. The main disadvantage of ring topology is the data flows only in one direction. And a break at a node in the network can affect the whole network.
d) Mesh Topology: In a Mesh Topology, each device of the network is connected to all other devices of the network. Mesh Topology uses Routing and Flooding techniques for data transmission.
The advantage of mesh topology is if one link breaks then it does not affect the whole network. And the disadvantage is, huge cabling is required and it is expensive.
Check out Latest Jobs for Network Engineer: Click here
Join Telegram Group of Daily Jobs Updates for 2010-2023 Batch: Click Here
If You Want To Get More Daily Such Jobs Updates, Career Advice Then Join the Telegram Group From Above Link And Never Miss Update.
Wipro Elite NLTH 2021 Registration has been Started: Click here
Accenture Hiring Freshers of Package 4.5 LPA Across India: Click here
Why You’re Not Getting Response From Recruiter?: Click here
Top 5 High Salary Jobs in India IT Sector 2020: Click here
How To Get a Job Easily: Professional Advice For Job Seekers: Click here
A Leadership Guide For How To Win Hearts and Minds: Click here
COVID-19 Live Tracker India & Coronavirus Live Update: Click here
Career Tips for Freshers: Top 7 Hacks To Land Your Target Job: Click here
Top 5 Best Indian Car Launches In December ahead: Click here
Feel Like Demotivated? Check Out our Motivation For You: Click here
Top 5 Best Mobile Tracking App in 2021 For Mobile & PC: Click here
5 Proven Tips For How To Look Beautiful and Attractive: Click here
Home Workouts During The Lockdown For Fitness Freaks: Click here